Who are the 57 members of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation? | Israel-Palestine conflict News | Al Jazeera

Understanding the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation: A Comprehensive Overview
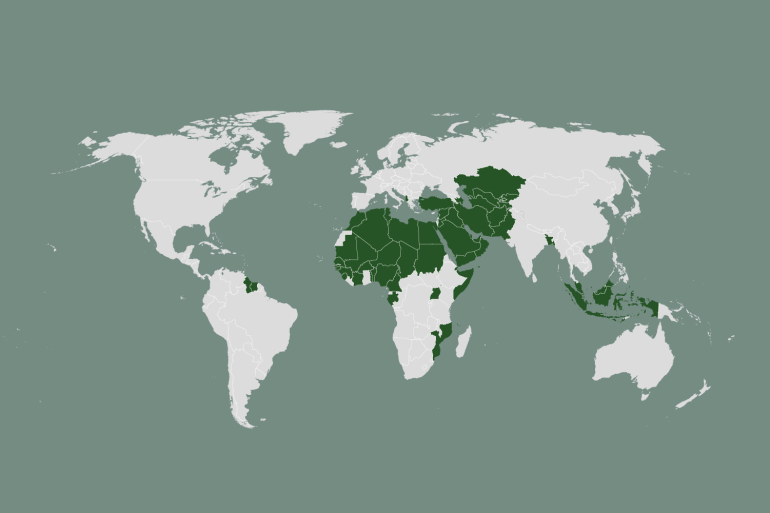
The Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) is a significant entity in the global political landscape, particularly concerning issues affecting the Muslim world. As of now, the OIC comprises 57 member states, representing a diverse array of cultures, economies, and political systems. This post explores the history, membership, and current initiatives of the OIC, particularly in light of recent developments in the Israel-Palestine conflict.
Historical Context of the OIC
The OIC was established in September 1969, primarily in response to an arson attack on the Al-Aqsa Mosque in Jerusalem. The founding meeting took place in Rabat, Morocco, where leaders from Muslim-majority nations gathered to create a body aimed at safeguarding Islamic holy sites and promoting political and economic solidarity among member states. Over the years, the OIC has evolved from its initial 30 members to the current 57, reflecting its growing influence and reach across the globe.
Membership Criteria and Expansion
Initially, the OIC had relatively lenient membership rules. Its original charter allowed any Muslim state to join with the approval of two-thirds of existing members. This provision enabled countries with significant Muslim populations, even if they did not have a Muslim majority, to become members. Nations such as Gabon, the Maldives, Mauritania, Uganda, Mozambique, Cameroon, Togo, Benin, the Ivory Coast, and Guinea-Bissau are examples of this inclusivity.
However, the OIC revised its charter in 2008, tightening the criteria for membership. Now, a country must be a member of the United Nations (with the exception of Palestine), have a Muslim-majority population, adhere to the OIC charter, and submit a formal application. Admission also requires consensus among all 57 members, making the process quite challenging.
Current Membership and Demographics
The OIC represents a significant portion of the global population, comprising over 2.1 billion people, which is approximately 26% of the world’s population. The combined GDP of OIC member states accounts for about 8% of the global economy. The organisation includes a diverse range of countries from various regions, including Asia, Africa, Europe, and the Americas.
Among the member states, there are notable exceptions and suspensions. Egypt, for instance, was suspended in 1979 after signing a peace treaty with Israel but was reinstated in 1989. Libya faced a similar fate during the 2011 uprising but was readmitted later that year. Syria was suspended in 2011 due to its ongoing civil war but was reinstated in 2023.
Recent Developments: The Israel-Palestine Conflict
The ongoing Israel-Palestine conflict remains a central focus for the OIC. Recently, representatives from the OIC convened in Doha to respond to Israel’s military actions, which included an attack on a Hamas office in Qatar that resulted in the deaths of six individuals. Qatari Prime Minister Sheikh Mohammed bin Abdulrahman bin Jassim Al Thani emphasized the need for the international community to hold Israel accountable for its actions and called for “fierce” and “firm” measures in response to the ongoing violence against Palestinians.
The OIC has consistently condemned Israeli military actions in Gaza and the occupied West Bank, advocating for immediate ceasefires and the protection of Palestinian civilians. The organisation’s leaders have stressed the importance of international accountability for what they describe as “Israeli crimes,” aiming to bring attention to the humanitarian crisis resulting from the conflict.
The Role of the Arab League
The OIC works closely with the Arab League, which consists of 22 member states primarily from the Arab world. This collaboration is particularly evident during emergency summits, such as the recent gathering in Doha. The Arab League and OIC members collectively represent nearly 500 million people, about 6% of the global population, and they play a crucial role in shaping a unified stance on critical issues, including the Israel-Palestine conflict.
Countries like Saudi Arabia, Iraq, Kuwait, the United Arab Emirates, Libya, and Algeria are part of both the OIC and the Organisation of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC), holding some of the largest proven oil reserves globally. Together, these nations produce approximately a quarter of the world’s oil, underscoring their economic significance.
Conclusion
The Organisation of Islamic Cooperation serves as a vital platform for Muslim-majority countries to collaborate on political, economic, and social issues. As the OIC continues to address pressing challenges, particularly regarding the Israel-Palestine conflict, its role in advocating for the rights of Muslims worldwide remains crucial. The diverse membership of the OIC reflects a broad spectrum of perspectives and experiences, making it a unique and powerful entity in international affairs.
Key Facts
– **Founded:** September 1969 in Rabat, Morocco.
– **Current Membership:** 57 member states.
– **Global Population Representation:** Over 2.1 billion people (approximately 26% of the world’s population).
– **GDP Representation:** About 8% of the global economy.
– **Recent Meeting Location:** Doha, Qatar, in response to Israel’s military actions.
– **Notable Membership Changes:** Egypt and Libya have experienced suspensions and reinstatements; Syria suspended in 2011, reinstated in 2023.
– **Collaboration:** Works closely with the Arab League, which has 22 member states.
Source: www.aljazeera.com

